Understanding common dog behaviors and their underlying causes is essential for building a strong bond with our furry friends.
In this article, we will continue to explore remaining common dog behavior and provide practical solutions to address them.
Related: 10 Common Dog Behaviors: Causes and Solutions (Part 1)
1. Aggression
What is “Aggression”?
Aggression in dogs can be caused by a variety of factors, including fear, territoriality, lack of socialization, previous traumatic experiences, or underlying medical conditions.
It is essential to identify the underlying cause to implement appropriate solutions effectively.
Solutions
- Consult a professional:
Aggression in dogs can be complex and potentially dangerous.
It is recommended to seek professional help from a qualified dog behaviorist or trainer experienced in handling aggression cases.
They can assess the situation, identify triggers, and develop a tailored behavior modification plan. - Create a safe environment:
Use a leash or secure fencing when necessary, especially in situations where aggression may be triggered, such as encounters with unfamiliar people or other animals. - Positive reinforcement training:
Implement positive reinforcement training techniques to redirect and modify aggressive behavior.
Reward your dog for calm and non-aggressive behavior using treats, praise, and affection. - Socialization and exposure:
Gradual and controlled exposure to various social situations can help desensitize your dog and reduce fear or aggression.
Introduce them to new people, animals, and environments in a positive and controlled manner, rewarding them for calm and non-reactive behavior. - Avoid punishment:
Punishment can escalate aggression and worsen the problem.
Instead, focus on positive reinforcement and redirecting your dog’s attention to more appropriate behaviors. - Consider medical evaluation:
In some cases, aggression may be linked to underlying medical conditions.
Consult with a veterinarian to rule out any potential health issues that may contribute to the aggression.
They can provide guidance on potential medical interventions or treatments. - Patience and consistency:
Stay patient and committed to the behavior modification plan.
Consistency in training methods and reinforcement is crucial for long-term success.

2. Leash Pulling
Understand “Leash Pulling”
Leash pulling is a common behavior in dogs, and it can be caused by several factors.
Some dogs pull on the leash due to excitement, a desire to explore, lack of leash training, or a strong instinct to lead.
Solutions
And here are some practical solutions:
- Proper leash training:
Teach your dog proper leash manners by using positive reinforcement techniques.
Start in a controlled environment with minimal distractions.
Reward your dog for walking beside you without pulling and provide treats or praise intermittently to reinforce the desired behavior. - Use appropriate equipment:
Consider using a front-clip harness or a head halter that gently redirects the dog’s attention back to you when they pull.
Avoid using choke collars, prong collars, or other aversive tools that may cause pain or discomfort. - Be consistent:
Consistency is key in training your dog to stop pulling.
Reinforce the desired behavior consistently and avoid rewarding them by allowing forward movement when they pull.
Encourage them to walk beside you and reward them for keeping a loose leash. - Change directions:
If your dog starts pulling, change direction abruptly.
This interrupts their forward momentum and redirects their focus back to you.
Reward them when they adjust their position to walk beside you. - Use positive distractions:
Engage your dog’s attention by using positive distractions such as treats or toys to redirect their focus from pulling.
Encourage them to walk beside you while keeping their attention on the reward. - Seek professional help if needed:
If leash pulling persists despite consistent training efforts, consider seeking guidance from a professional dog trainer.
They can assess the situation, provide additional techniques, and address any underlying issues that may contribute to the pulling behavior.

3. Food Stealing
Cause of “Food Stealing”
Food stealing behavior in dogs can stem from various causes, including hunger, lack of food or proper nutrition, learned behavior, attention-seeking, or a result of previous reinforcement.
Solutions
Solution for this situation:
- Prevention:
Ensure that food is securely stored and inaccessible to your dog when you’re not present.
Avoid leaving food unattended on countertops or within your dog’s reach. - Proper feeding routine:
Establish a consistent feeding routine for your dog, with designated meal times and appropriate portion sizes.
By providing regular and balanced meals, you can address any potential underlying hunger issues that may contribute to food stealing behavior. - Teach the “Leave It” command:
Train your dog to respond to the “leave it” command, which teaches them to avoid or move away from food that is not intended for them.
Practice this command in controlled training sessions and gradually increase difficulty by using higher-value treats or food items.. - Reward and reinforce positive behavior:
When your dog demonstrates appropriate behavior around food, such as waiting patiently for their own meal or ignoring food that is not theirs, reward and praise them.
Positive reinforcement helps reinforce desired behavior and encourages them to make the right choices. - Supervise and manage mealtimes:
When feeding your dog, supervise their mealtime to prevent any attempts to steal food.
If necessary, separate multiple dogs during mealtimes to avoid competition or stealing behaviors.

4. Excessive Licking
Understand “Excessive Licking”
Excessive licking behavior in dogs can have various causes, including anxiety, boredom, allergies, pain or discomfort, compulsive behavior, or a sign of an underlying medical condition.
Understanding the underlying cause is essential in determining the appropriate solution.
Solutions
Some tips for you:
- Identify and address any underlying medical issues:
If your dog’s excessive licking appears to be focused on a specific area of their body, consult with a veterinarian to rule out any medical conditions that may be causing discomfort or irritation.
Treat any identified medical issues accordingly. - Provide mental and physical stimulation:
Boredom can lead to excessive licking behavior.
Ensure that your dog receives sufficient mental and physical exercise to keep them engaged and entertained. - Address anxiety or stress:
Excessive licking can be a manifestation of anxiety or stress.
Identify potential triggers and provide your dog with a calm and secure environment.
Use techniques such as positive reinforcement training, calming aids (e.g., pheromone diffusers), or consult with a professional behaviorist to address anxiety-related behaviors. - Provide appropriate chew toys:
Sometimes, excessive licking can be a result of oral discomfort or a desire to chew.
Offer a variety of safe and appropriate chew toys to satisfy their chewing instincts and provide relief for their oral discomfort. - Training and behavior modification:
If excessive licking persists despite your efforts, consider seeking guidance from a professional dog trainer or behaviorist.
They can assess the situation, develop a behavior modification plan, and provide specialized techniques to address the excessive licking behavior effectively.

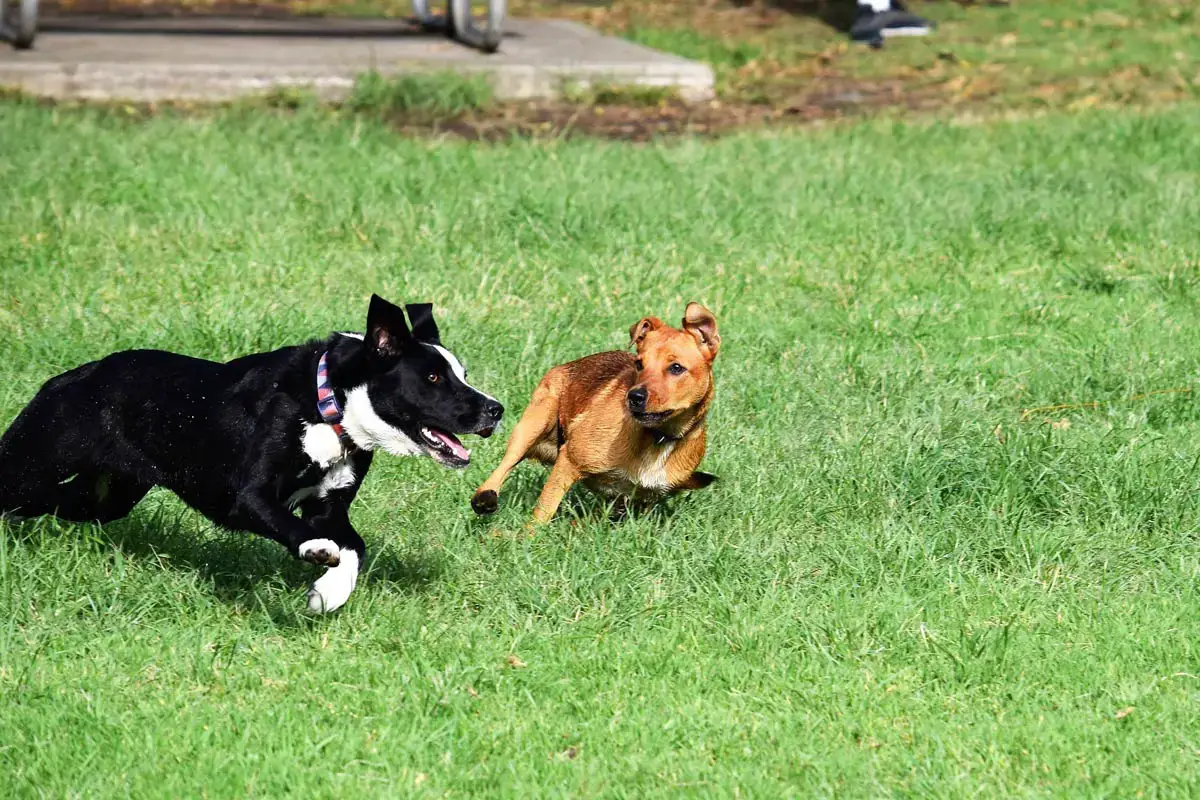
5. Chasing
What is “Chasing”?
Chasing behavior in dogs can be instinctual and can stem from a variety of causes, including predatory instincts, high energy levels, lack of proper training and socialization, or a response to stimuli such as moving objects or animals.
Solutions
- Recall training:
Teach your dog a reliable recall command, such as “come” or “here.”
Practice this command in controlled environments, gradually increasing distractions.
Use high-value treats or rewards to reinforce their response to the recall command, redirecting their focus from chasing. - Leash and boundary training:
Keep your dog on a leash or in a securely fenced area when outside.
This prevents them from chasing after moving objects, animals, or people.
Consistently reinforce the boundaries to help them understand that chasing is not permitted. - Physical exercise and mental stimulation:
Ensure that your dog receives sufficient physical exercise and mental stimulation to help alleviate excess energy and prevent boredom. - Professional guidance:
If your dog’s chasing behavior is persistent, intense, or poses a risk to their safety or the safety of others, consider seeking guidance from a professional dog trainer or behaviorist.
They can assess the situation, provide specialized training techniques, and develop a behavior modification plan tailored to your dog’s needs.

Conclusion
Understanding common dog behaviors and their underlying causes can help dog owners address problematic behaviors and strengthen their relationship with their canine companions.
While training and management strategies can help address many behaviors, some may require professional intervention.
By working with a professional trainer or behaviorist, you can develop a personalized plan to address your dog’s behavior and improve their quality of life.
Related:
How to Training a Dog – 10 Essential Dog Training Tips for New Owners
Training Tips: Why and How to Socialize Your Dogs or Puppies